The novel coronavirus was first detected in Wuhan City, Hubei province, China in December 2019 and since then rapidly spread across the world. On 11 March, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared COVID-19 a pandemic.
As a global organization representing the cardiovascular community, WHF is committed to offering the latest evidence of the outbreak and ensuring everyone is aware of the necessary measures to protect themselves and others in order to slow the spread of the disease.
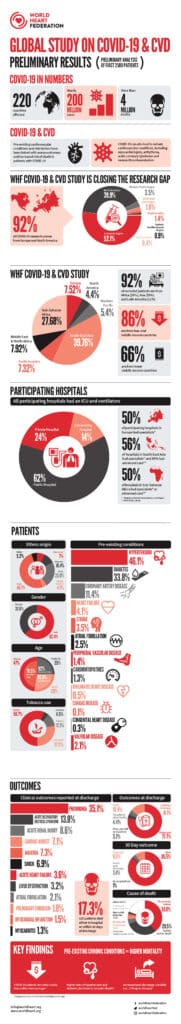
Learn more about the WHF Global Study on CVD and COVID-19.
Signs & symptoms
Symptoms of the infection may appear 2-14 days after exposure and include:
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Fever
If you develop emergency warning signs, get medical attention immediately. Warning signs may include:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Persistent pain or pressure in the chest
- New confusion or inability to arouse
- Bluish lips or face
Research suggests that some individuals are more vulnerable to the worst outcomes of the virus:
- Older adults
- People who have serious chronic medical conditions like diabetes or heart disease
- Maintain at least 1-metre distance between yourself and anyone who is sick.
- Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing.
- If soap and water are not available, use a hand sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol.
- Clean and disinfect your home to remove germs.
- Stay informed on the latest developments about COVID-19.
People of all ages can be infected by the new coronavirus. However, the virus poses a particular risk to people over the age of 60 and those with underlying medical conditions, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Chronic respiratory disease
- Cancer
To avoid infection, we recommend you to:
- Continue to take your medication and follow medical advice
- Secure a one month supply of your medication or longer if possible
- Keep a distance of at least one metre from people with a cough, cold or flu
- Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds
- Stay at home if possible
- Follow the instructions of the Department of Health and local authorities in your country
Remain aware of your health state. If you experience severe symptoms (shortness of breath, fever), call your doctor or a hospital immediately. Explain to them that you are calling in relation to the new coronavirus and that you are at high risk.
Look after your mental health and well-being too. If you need to stay home for a prolonged period, try maintaining a daily routine that prioritizes taking care of yourself.
Considering the greater risk for populations in impoverished settings, WHF has developed a series of guidelines on COVID-19 prevention and control in low-income countries.
A study published in The Lancet on 14 March 2020 reviewed the psychological effects of quarantines during disease outbreaks. The report takes information from another study published in 2004 during the SARS outbreak, which revealed that quarantined hospital staff was more likely to report exhaustion and irritability, anxiety and depression.
To protect the mental health of these professionals, China’s National Health Commission released guidelines for psychological care during the pandemic and WHO shared several mental health tips for healthcare practitioners, which includes:
- Ensure rest during work or between shifts, eat sufficient and healthy food and engage in physical activity.
- Avoid using unhelpful coping mechanisms such as tobacco or alcohol.
- Some workers may experience avoidance by their family or community due to stigma or fear. If possible, stay connected with your loved ones. Turn to your colleagues and your manager for social support.
- Team leaders should provide good quality communication and accurate information updates to all staff. Ensure you initiate, encourage and monitor work breaks.
WHF regards the vaccine as a critical tool in our fight to ward off the disease and focus on managing and preventing the heart conditions that further complicate the lives of those with COVID-19.
In supporting the global effort to address the pandemic, WHF reiterates that successful vaccine roll-out must include those most vulnerable, either because of health risks, on-the-job exposure, or socioeconomic status, a particular concern in low and middle-income countries.
As a signatory to the WHO Declaration on vaccine equity, WHF urges others to get involved and spread the word for #VaccinEquity.
The Human Side of the Pandemic

COVID-19 across the spectrum: South Africa
Prof Liesl Zühlke

COVID-19 across the spectrum: Spain
Juan Cosin Sales

COVID-19 across the spectrum: Bangladesh
Dr. Ferdous Hakim

Understanding links between COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease in Argentina
Dr Ezequiel J. Zaidel

Acting in the face of uncertainty
Dr Andrea Fernandes das Neves

A profession that is impossible to perform if it is not vocational
Teresa Miguel Trasobares

Emergency cardiac care in the time of COVID-19
Shirley Ingram

Coronavirus pandemic and me, my family and my country
Dr Ferdous Hakim

Adversity is the mother of adaptation
Dr Lucrecia M. Burgos

Focusing on healing both the body and the spirit
Dr Eduardo Chuquiure-Valenzuela
Latest News
2022 Emerging Leaders cohort: CVD and Infectious diseases
The 2022 Emerging Leaders Seminar took place in Buenos Aires, Argentina and brought together a team of Emerging Leaders from 17 countries across five continents. Between 17 and 21 October 2022, 24 participants from 17 countries attended the eighth WHF Salim Yusuf Emerging Leaders Seminar in Buenos Aires, Argentina. The Emerging Leaders have joined a […]
Chagas Disease
COVID-19
Influenza
Strengthening health emergency preparedness and response in the WHO South-East Asia Region
This is a statement made at the 75th Session of the World Health Organization RCM for the SEARO Region. Honourable Chair, distinguished delegates, The World Heart Federation, supported by South East Asia Regional NCD Alliance, Healthy India Alliance and NCD Alliance, thank you for this opportunity to address the Regional Committee on one of the […]
COVID-19
Strengthening WHO Preparedness and Response to Health Emergencies: WHF Update
From the earliest days of the COVID-19 pandemic, the World Health Organization (WHO) has been deeply involved in efforts to understand, mitigate, and strengthen health systems in relation to the coronavirus. In addition to technical undertakings and in-country support, the Governing Bodies of the WHO have worked to create global health policy to both counter […]
COVID-19
Addressing emergency preparedness at WHA74 special session
This is a statement made at the 74th World Health Assembly Special Session (29 November – 1 December 2021) on Agenda Item 2: Consideration of the benefits of developing a WHO convention, agreement or other international instrument on pandemic preparedness. Honourable Chair, Distinguished Delegates, Following careful review, the WGPR[1] has concluded that key aspects […]
COVID-19